Notes of chapter: Stars and the Solar System are presented below. Indepth notes along with worksheets and NCERT Solutions for Class 8.
(1)Celestial objects-
Celestial objects are the natural objects located outside the Earth atmosphere or in sky.
Eg :-The stars, the Moon, the sun, the planets etc.
(2) The Moon-
Phases of the moon-
The various shapes of the bright part of the Moon as seen during a month are called phases of the Moon.

(i)Full moon day-
Full moon day occurs when the Earth is located in between the Moon and the Sun and on that day whole moon is visible. It happens after every fifteenth day.
(ii)The new moon day-
The new moon day occurs when the moon is located in between of the Sun and the earth and on that day the moon is not visible. It happens after every fifteenth day.
(iii)The crescent moon-
The crescent moon is the small portion of the bright side of the moon that is visible after new moon day and before full moon day.
The size of the illuminated part of the moon visible from the earth increases each day after the new moon day. After the full moon day, the sunlit art of the moon visible from the Earth decreases in size every day.
(iv) The time period between one full moon day to next full moon day is longer than 29 days. Therefore, it is considered as a month in many calendars.
(v)The moon does not produce its own light but it is visible due to light receive from the sun and the sunlight reflected to us.

Revolutions of the Moon-
(i) The moon revolves around the Earth and the Earth along with the Moon revolves around the Sun.

(ii) The time taken in one rotation by the Moon on its axis is almost equal to time taken to complete one revolution around the earth, ie, approximately 27 days.
The Moon’s Surface-
(i) The Moon’s surface is dusty and barren.
(ii)There are many caters on the Moon.
(iii) The Moon has many high mountains.
(iv) The Moon has no water and no atmosphere. Therefore, there is no life on the Moon.
(3) The stars-
Stars are the most recognised body of the galaxy that produces heat and light.
Eg:- The Sun
Characteristics of the stars-
(i) Stars illuminated their own.
(ii) Stars are big in size.
(iii) The Sun is also a star. But it appears to be bigger than stars. Stars are millions of times farther away than the Sun. Hence, stars appear to be smaller than the Sun.
(iv) Stars present in the sky during day time. But we can not see them because of the bright sunlight.
(v) Stars apperas to move from the East to the West.
(vi) The pole star is situated in the direction of the earth’s axis. It does not appear to move.
(vii) The Sun is nearly 150,000,000 kilometers (150 million km) away from the Earth.
(vii) The next nearest star is Alpha Centauri which is at a distance of about 40,000,000,000,000 km from the Earth. Some stars are even further away.
(ix) Light year is a unit to measure large astronomical distances travels in one year.
1 light year = 9.46 trillion km
(4) Constellations-
Stars forming a group that have a recognisable shape is called a constellation.
Eg:- Ursa major, Orion, Leo Major etc.

(i) The shape of the constellations resembles objects familiar to ancient people who discover constellations. Sometimes one constellation has different names because the constellation is identified by people of different regions of the Earth. Hence, they called the same constellation with different names.
(ii) A constellation can have large number of the stars. But we can see only bright stars with necked eyes.
(iii) Distances of all stars of a constellation are different from each other. These are in same line of sight on the sky.
Ursa Major-
(i) It is also known as Big Dipper, the great Bear or the Saptarshi.
(ii) Dipper is used for drinking purposes in ancient time. Therefore, it is called the Big Dipper.
(iii) In India, the Saptarshi constellation is named after seven rishis.
(iv) It is a group of seven stars. It resembles with a big ladle or a question mark.
(v)There are three stars in the handle of the ladle and four in its bowl.
(vi) Constellation appears to move in the sky from east to west.

Pole star-
(i) Pole star is a bright star which is located in the north direction from the end of the Ursa Major. Two stars of the Ursa Major appear to be in straight line. Follow that line and find pole star in North direction.

(ii) The pole star does not move.
(iii) Pole star is visible only in Northern hemisphere. It can not be seen from the southern hemisphere.
Orion-
(i) It is one of the most magnificent constellations in the sky which can be seen in late evenings of winter.
(ii) It is a group of seven and eight stars.
(iii) It is also known as hunter.
(iv) The three middle stars represent the belt of the hunter. The four bright stars appear to be arranged in the form of a quadrilateral.

Sirius-
(i) It is the brightest star in the sky.
(ii) It is located near Orion.
(iii) Imagine a straight line which is passing through the three middle stars of Orion. This line will reach a bright star towards east direction is called as Sirius.

Cassiopeia-
(i) It is located in the Northern sky.
(ii) It can be visible in early part of the night during winter.
(iii) Its shape is recognise with letter W or M.

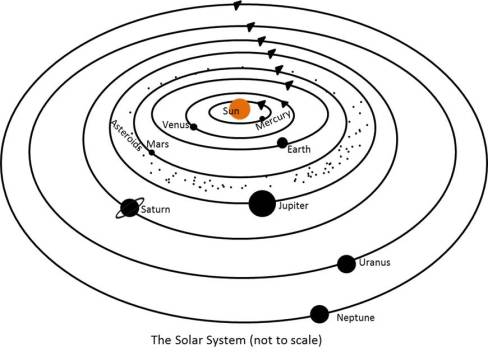
Solar System-
The solar system is the system where the celestial bodies such as planets, comets, asteroids and meteors revolves around the Sun because of gravitational attraction.
(i) The earth is also a planet and revolves around the Sun. The other members of the planets are – Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune.
(ii) The International Astronomical Union (IAU) redefined planet in 2006. Since then Pluto is not considered as planet.
The Sun-
(i) The sun is the nearest star from the Earth.
(ii) It continuously emits heat and light due to chemical reactions in it.
(iii) The Sun is the source of heat and light for all planets.
The planets-
(i) These do not have their own light. They do not reflect the sunlight that falls on it from the sun.
(ii) These always keep changing their positions with respect to the stars.
(iii) An orbit is a definite path in which planets revolves around the Sun.
(iv) The time taken by a planet to complete one revolution around the Sun is called its period of revolution that increases as the distance of the planet increases from the Sun.
(v) The time taken by a planet to complete one rotation on its axis is called period of rotation.
Satellite-
Any celestial body that revolves around another celestial body is called satellite.
Types of Satellite-
(i) Those satellites that are natural celestial body and revolve around another celestial body are known as the natural satellite.
Eg:– The Moon revolves around the Earth
(ii) The manmade satellites that revolve around the planets in order to collect information are called artificial satellite.
Eg:- Aryabhatta (First Indian satellite), INSAT, IRS, Kalpana -1, EDUSAT etc.
(a) Artificial satellites are launched from the Earth and revolve much closer to the Earth than earth’s natural satellite, the Moon.
(b) Artificial satellites are used for forecasting weather, transmitting television and radio signals. These are also used for the telecommunication and remote sensing.
Planets of the solar system-
Mercury (Budh)-
(i)It is the nearest planet to the Sun.
(ii) It is the smallest planet of the solar system.
(iii) It cannot easily observe as it is the nearest planet to the Sun. It hides in glare of the Sun. Therefore, the Mercury can visible just before the sunrise and just after the sunset, near the horizon where trees and the buildings do not obstruct view of it.
(iv) It does not have its own satellite.
Venus-
(i) It is the nearest to the Earth.
(ii) It is the brightest planet in the night sky.
(iii) It is known as morning or evening star though it is a planet. It appears in the eastern sky before sunrise. Sometime it appears in the western sky just after sunset.
(iv) It has no moon or satellite of its own.
(v) It rotates from east to west.
The Earth-
(i) It is the only planet where life is possible.
(ii) It is at the right distance from the Sun. Therefore, it has right temperature range.
(iii) It also has water, suitable atmosphere and a blanket of ozone.
(iv) It rotates from west to east.
(v) The Earth appears blue green from the sky due to reflection of light from water and landmass.
(vi) The axis of rotation of the Earth is not perpendicular to the plane of its orbit. The tilt is responsible for the change of the seasons on the earth.
(vii) The Earth has only one Moon.
Mars (Mangal)-
(i) It is the second smallest planet of the solar system.
(ii) It appears slightly reddish, therefore it is called red planet.
(iii) It has two small natural satellites.
Jupiter-
(i) It is the largest planet of the solar system. About 1300 earths can be placed inside the Jupiter.
(ii) It is about 318 times heavier than that of the Earth.
(iii) It rotates very rapidly on its axis.
(iv) It has a large number of satellites.
(v) It also has faint rings around it.
(vi) It can be easily recognised by its brightness, if we see it by telescope.
(vi) It has four moons.
Saturn (Shani)-
(i) It appears yellowish in colour.
(ii) It has beautiful rings around it which can be visible by a telescope.
(iii) It has a large number of satellites.
(iv) It is the least dense among all planets. Its density is less than water.
Uranus and Neptune-
(i) These are the outermost planet of the solar system.
(ii) Uranus also rotates from east to west.
(iii) Uranus has highly tilted rotational axis. Therefore, it appears to roll on its side in its orbital motion.
Inner planets are those planets which are very close to the sun and have very few moons.
Eg:- Mercury, Venus, Earth and Mars
Outer planets are those planets which are very far from the Sun, have rings around them and have large number of moons.
Eg:- Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune
Some other members of the solar system-
(i) Asteroids are small, rocky objects which orbits the Sun like planet but smaller than planets. They are located in the gap between the mars and the Jupiter.

(ii) Comets-
Comets are the icy small balls made up of dust and rocks, orbits in highly elliptical orbits around the Sun and appear generally as a bright head and a long tail which is always directed away from the sun.

(a) The length of the tail grows in size as we approached to the sun.
(b) Many comets appear periodically like Halley comet which appears after every 76 years. It appears in 1986.
(iii) Meteors and meteorites are small objects that occasionally enter the earth’s atmosphere at very high speed and glow and evaporate due to friction of atmosphere that leave a bright streak for a very short time.
(iv) The large meteors which can reach to the Earth before evaporating are known as meteorite. These are very helpful for investigating the nature of the material from which our solar system was formed.
(v) Meteor shower is a storm or rain of meteor occurs at regular intervals each year, comes from a particular region of sky and caused when the Earth passes through a large number of meteoroids.
Helping Topics
Differences between the Full Moon Day and New Moon Day
Differences between the Inner and Outer Planet