Notes of chapter: Practical Geometry are presented below. Indepth notes along with worksheets and NCERT Solutions.
Practical Geometry-
A branch of mathematics which is related to different shapes, angles, lines and their properties is known as geometry. The use of properties of geometry is called practical geometry.
(1)Construction of a parallel line using ruler and compasses only
Step 1-
Draw a line ‘l’ and took a point ‘A’ outside ‘l’.

Step 2-
Take any point B on l and join B to A.

Step 3-
With B as centre and a convenient radius, draw an arc cutting l at C and BA at D.

Step 4-
Now with A as centre and the same radius as in Step 3, draw an arc EF cutting AB at G.

Step 5-
Place the pointed tip of the compasses at C and adjust the opening so that the pencil tip is at D.
Step 6-
With the same opening as in Step 5 and with G as centre, draw an arc cutting the arc EF at H.

Step7-
Join AH and draw a line m.


(2)Construction of Triangles
(i) Constructing a triangle when the lengths of its three sides are known (SSS Criterion)
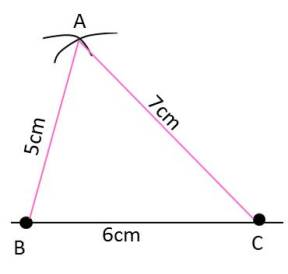
Eg.:- Construct a triangle ABC, given that AB = 5cm, BC = 6 cm and AC = 7 cm.
Ans-
Step 1-
Draw a line segment BC of length 6 cm.

Step 2 –
With B as center, draw an arc of radius 5 cm.

Step 3-
With C as center, draw an arc of radius 7 cm.

Step 4-
Mark the point of intersection of arcs as A. Join AB and AC.ABC is required triangle.
(ii)Constructing a triangle when the lengths of two sides and the measure of the angle between them are known (SAS Criterion)
Eg.-Construct a triangle PQR, given that PQ = 3 cm, QR = 5.5 cm and PQR = 600
Step1-
Draw a line segment QR of length 5.5 cm.

Step 2-
At Q,draw QX making 600 with QR.

Step 3-
With Q as center, draw an arc of radius 3 cm. It cuts QX at the point P.

Step 4-
Join PR, ΔPQR is mow obtained.

(iii)Constructing a triangle when the measures of two of its angles sand the length of the side included between them is given.(ASA criterion)
Eg- Construct XYZ if XY = 6cm, mXYZ = 1000 and mZXY = 300
Ans-
Step 1-
Draw XY of length 6cm.

Step 2-
At point X, draw a ray XP making an angle of 300 with line XY.

Step 3-
At point Y, draw a ray YQ making an angle of 1000 with line YX.

Step 4-
Z has to lie on both the rays XP and YQ. So, the point of intersection of the two rays is Z.
ΔXYZ is required triangle.

(iv)Constructing a right- angled triangle when the length of one leg and its hypotenuse are given (RHS Criterion)
Eg- Construct LMN, right-angled at M, given that LN = 5cm and MN = 3cm.
Ans-
Step1-
Draw MN of length 3 cm.



Step 3-
With N as center, draw an arc of radius 5 cm.

Step 4-
L has to be on the perpendicular line MX as well as on the arc drawn with centre N.
Therefore,
L is the meeting point of these two.

ΔLMN is now obtained.
(3) Construction of quadrilateral
(i) When the lengths of four sides and a diagonal are given
Eg :- Construct a quadrilateral PQRS where PQ = 4 cm, QR = 6cm, RS = 5cm, PS = 5.5cm and PR = 7cm.
Step 1-
Draw rough sketch of required quadrilateral PQRS.

Step 2-
Draw diagonal PR = 7cm.

Step 3-
Draw an arc of 4 cm with P as a centre.

Step 4-
Draw an arc of 6 cm with R as a centre.

Step 5-
Mark point of intersection as Q and join point Q to point P and R.

Step 6-
Draw an arc of 5.5cm with P as a centre in other side of the diagonal.

Step 7-
Draw an arc of 5 cm with R as centre.

Step 8-
Mark point of intersection as S. Join point S to point P and R.
We get required quadrilateral PQRS.

(ii) When two diagonals and three sides are given
Eg :- Construct a quadrilateral ABCD, given that BC = 4.5 cm, AD = 5.5 cm, CD = 5 cm the diagonal AC = 5.5 cm and diagonal BD = 7cm.
Step 1-
Draw rough sketch of required quadrilateral ABCD.
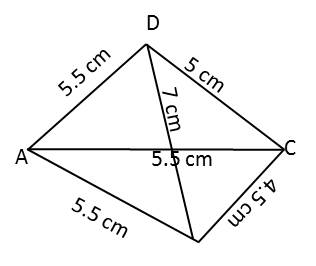
Step 2-
Draw a diagonal AC = 5.5cm.

Step 3-
Draw an arc of 5.5 cm with A as centre.

Step 4 –
Draw an arc of 5 cm with C as a centre.

Step 5 –
Mark point of intersection as D. Join the point D with point A and point C.

Step 6-
Draw an arc of 7 cm with D as a centre.

Step 7 –
Draw an arc of 4.5 cm with C as centre.

Step 8-
Mark point of intersection as B. Join point B to point A, C and D.
ABCD is required quadrilateral.

(iii)When two adjacent sides and three angles are given
Eg:- Construct a quadrilateral MIST where MI = 3.5 cm, IS = 6.5 cm, M = 75º ,
∠I = 105º and ∠S = 120º
Step 1-
Draw rough sketch of required quadrilateral MIST.
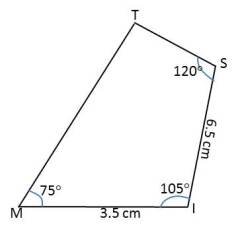
Step 2 –
Draw a line MI = 3.5cm.

Step 3-
Draw an angle of 1050 at point I.

Step 4-
Take 6.5 cm distance on IX and take point S on it. Draw an angle of 1200 at point S.

Step 5-
Draw an angle of 750 at point M. Line will intersect SY at point T. Join the Point T and M.
MIST is required quadrilateral.
First draw 900 angle at point M applying same method at point I. Now bisect the 300 angle inside 900. We get 750. Join the line and make quadrilateral MIST.

(iv) When three sides and two included angles are given
Eg:- Construct a quadrilateral ABCD, where AB = 4cm,BC = 5cm, CD = 6.5 cm and ∠B = 105º and ∠C = 80º .
Step 1-
Draw rough sketch of required quadrilateral ABCD.

Step 2-
Draw a line BC of 5 cm length. Draw an angle of 105º at point B.Join point B to A at the length of 4 cm.

Step 3-
Draw an angle of 80º at point C. Draw an arc of 6.5 cm from point C. Mark this point as D.

Step 4-
Join point D to point A. Quadrilateral ABCD is required quadrilateral.

Helping Topics