Notes of chapter: Circles are presented below. Indepth notes along with worksheets and NCERT Solutions of class 9.
(1) Circle-
A circle is the collection of all points in a plane, which are equidistant from a fixed point in the plane.

Figure of circle is showing below-
O is a fixed point.
Parts of the circle-
(i) Center-
The fixed point of circle is known as center.
Eg:- O is center of the circle.

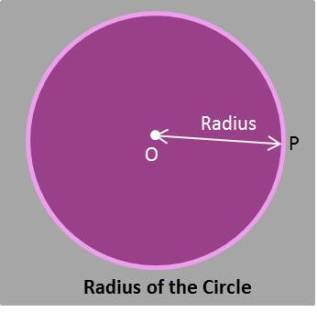
(ii)Radius-
The distant from center of the circle to the boundary of circle is known as radius.
Eg:- OP is distance from center and boundary of the circle.
(iii) Chord-
The line segments which touches boundary of the circle is known as chord.
Eg:- AB is a chord of the circle.

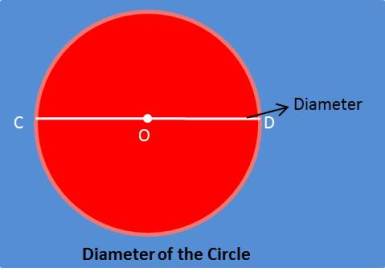
(a) Diameter-
The chord which passes from the center is known as diameter.
Eg:- CD is a diameter of the circle.
Properties of the diameter-
(A) It is longest chord of the circle.
(B) All diameters of a circle are equal in lengths.
(C) Diameter is twice of the radius of the circle.
Diameter = 2radius
(iv)The part of a circle between two points is called an arc.
Eg:- In figure below, points P and Q divides circle in two parts which are known as arcs. One arc is PAQ and second arc is PBQ.

Types of arcs-
(a) Major arc –
The longer part of a circle between two points on a circle is known as major arc.
Eg:- In figure below, PRQ is a major arc.

(b) Minor arc-
The shorter part of a circle between two points on a circle is known as minor arc.
Eg:- In figure below PQ is a minor arc.

(c)Semicircle-
When P and Q are ends of a diameter then both arcs are equal and called as semicircle.
Eg:- In figure below P and Q are ends of diameter PQ. Therefore, PRQ and PSQ are equal and semicircle.



(vi) Segment-
The region between the chord and the arc is called as segment of the circle.
Eg:- In figure below, circle has two segments.

Types of the segments –
(a) Major segment-
The region between the chord and the large arc is called as major segment of the circle.
Eg:- In figure below PRQ is a major segment.

(b) Minor segment-
The region between the chord and the small arc is called as minor segment of the circle.
Eg:- In figure below PSQ is a minor segment.

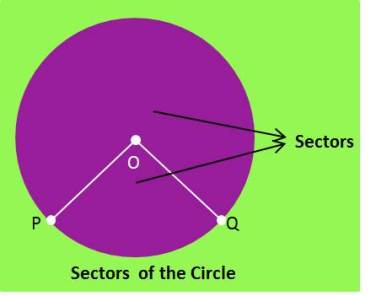
(vii)Sector-
The region between an arc and two radii is known as sector of a circle.
Eg:- In figure below, circle has two sectors.
Types of sector-
(a) Major sector-
The region between major arc and two radii is known as major sector of a circle.
Eg:- In figure below, circle has major sector.

(b)Minor sector-
The region between minor arc and two radii is known as minor sector of a circle.
Eg:- In figure below, circle has minor sector.

(2) A circle divides a plane on which it lies into three parts.
(i)The region of plane inside of the circle is known as interior of the circle.
Eg:- In figure below, interior of the circle is presented.
(ii)The region of plane outside of the circle is known as exterior of the circle.
Eg:- In figure below, exterior of the circle is presented.
(iii)The boundary of the circle is known as circle.
Eg:- In figure below, circle is presented.
The circle and its interior make up the circular region.














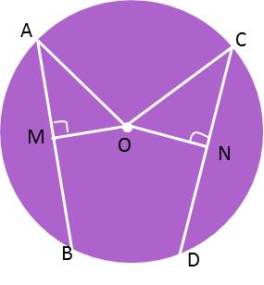
Take three non – collinear points A, B and C.
Draw perpendicular bisectors PQ and RS of AB and BC respectively.
Let these perpendiculars bisectors intersect at point O. ( Two lines intersect only at one point.)
Point O lies on the perpendicular bisector PQ of AB,
OA = OB …(1)
(Every point of perpendicular PQ is equidistance from end points of AB)
Similarly, point O lies on the perpendicular bisector RS of BC,
OB = OC ( every point of perpendicular PQ is equidistance from end points of AB)…(2)
OA = OB = OC (From equation 1 and 2)
Therefore, we can draw a circle with centre O which will pass through point A, B and C.
Hence, proved.

























Helping Topics