Notes of chapter: Soil are presented below. Indepth notes along with worksheets and NCERT Solutions for Class 7.
(1) Soil-
Soil is black or dark brown upper layer of the Earth which is full of minerals and nutrients and responsible for the growing of plants.
(2) Importance of soil-
(i) It holds the root of the plant firmly.
(ii) It supplies water and nutrients to the plant through roots.
(iii) Many organisms live in the soil.
(iv) It is necessary for agriculture.
(v) The earthy fragrance of the soil after the first rain is always refreshing.
Experiment 1
Collect some soil samples and examine them with the help of the lens. Fill your result in the table given below:
Table: Results of soil examination-
| S. N. | Soil source | Plants | Animals | Any other observations |
| 1. | Garden soil | Grass, rose, neem etc. | Ant, Grasshoppers, earthworms etc | Brown, no stones |
| 2. | Soil from the roadside | Sometimes grass found or some tree of banyan, neem etc | Ant, | Light brown, dry, small size stones |
| 3. | Soil from the area where construction is going on | Some times grass found only | Ant | Light brown, stones ,dry |
| 4. | Soil from the hills | Grass, plants, trees | Ant, Grasshopper, worms etc. | Brown, very small size stones in less quantity |
(3) Polythene bags, plastics, waste products, chemicals and pesticides pollute the soil. They kill the organisms living in the soil. So, polythene bags should not be used. Waste products and chemical should be treated before they are released into the soil. Pesticides should be used minimum.
(4) Soil is composed of many layers.
Experiment 2
Take a little soil and powder it with hand. Take a glass and fill it three quarters with water. Put a soil it. Stir it and leave it for some time. You will see layers of soil in the glass. You will find gravel, sand clay, water and humus separate layers in the glass.

(5) Humus –
The dark brown organic material which is obtained from the decomposition of the leaves and animals waste is called humus. It gives nutrients to soil.
(6) Weathering –
Soil is formed by the processes of weathering. The processes in which rocks are break down by the action of wind, water and climate to form soil is called weathering. The nature of soil depends upon the originator rock and the vegetation grows on it.
(7) Soil profile-
A vertical section through different layers of the soil from the surface to the parent rock is called soil profile.
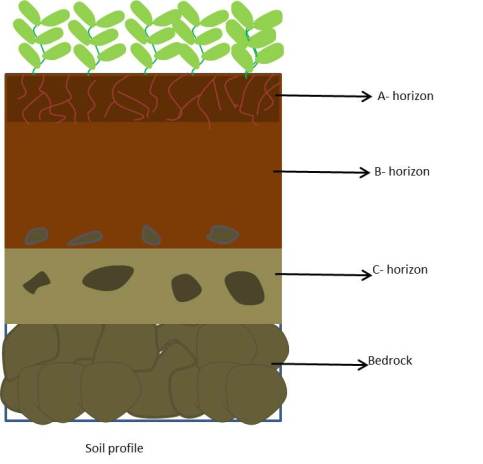
(8) Horizons-
Horizons are the different layers of the soil that differs in texture, colour, depth and chemical composition.
(9) We can see the layers of the soil while digging for wells or for foundation of the buildings. Layers can also be seen at the sides of a road on a hill or at a steep river bank.
(10) The top most layer of the soil is soft, porous, can retain more water, dark in colour and rich in nutrients which make soil fertile is known as topsoil or the A-horizon.
(11) Importance of the topsoil-
(i)The worms, rodents, moles and beetles live in topsoil.
(ii) The roots of small plants are fixed in the topsoil.
(12) B – horizon-
The layer next to topsoil layer has more minerals and less humus, harder and more compact than topsoil layer is known as B-horizon. It is also called middle layer.
(13) C-horizon-
The layer next to B-horizon is made up of small lumps of rocks with cracks and crevices, is known as C- horizon.
(14) Bedrock –
The layer next to C-horizon is hard and difficult to dig with a spade is known as bedrock.
(15) Parent rock-
The rock which produces small particles of various materials as sand and clay is known as parent rock.
(16) The mixture of rock particles, humus, living and dead organisms (bacteria, earthworm etc.) is also called the soil.
(17) Types of soil-
Soil is classified on the basis of the proportion of particles of various sizes.
Different soil types are showing below in table.
Soil Types-
| S.N. | Soil type | Size of particles | Remarks |
| 1. | Sandy soil | Higher proportion of large particles
Lower proportion of fine particles |
Spaces between particles
Spaces filled with air(aerated soil) Water can drain through the spaces(dry soil) |
| 2. | Clayey Soil | Lower proportion of small particles
Higher proportion of fine particles |
Being small particle pack tightly
Can hold water – heavy Little space for air |
| 3. | Loamy | Small and fine particles are in equal proportion | Mixture of sand, clay and silt (occurs as a deposit in river beds).
Size of silt particles is between sand and clay. Has humus and right water holding capacity for plant. |
Experiment 3
Collect samples of sand, clayey and loamy soils. Remove stone, grass etc. from them. Now knead them with water. Make a ball from each of them. Roll them and make separate cylinder from them. Make rings from them. Let them dry. The ring from the clayey soil will be good in shape and become hard after drying because of the water content in it and close particles. Sand soil has large particle which loosely fit together. So, toy makes from it crumbles after drying. Loamy soil has small and tighter fit particles together in comparison of sand soil. But its toy also crumbles after drying. So, clayey soil is the best for toy making.



Toys from soil
(18) Properties of soil-
(i) Percolation rate-
Percolation rate of the soil is the amount of water passes through the pores of the soil with in the soil matrix or layers of soil. It is usually expressed in milliliter per minute.
Experiment 4
Make three teams A, B and C. You need 3 hollow pipes of same diameter for each team. Put the cylinder 2 cm deep in soil. Pour 200 ml water in it. Note the time when you start pouring water. When all the water percolated and cylinder emptied note the time again. Do not allow the water to spill over or run out side the cylinder.

Calculate the rate of percolation by using the following formula:
Percolation rate (ml/min) = amount of water (ml)/percolation time (min)
(ii) Moisture in soil is the amount of water in the soil.
Experiment 5
Take a boiling tube and put two spoon soil in it. Now heat it. On heating water of soil evaporates, moves up and condenses on the cooler inner walls of the upper part of the tube.

Effects on soil after heating are given below-
(a) Soil lost its organic matter.
(b) Heat reduced porosity of the soil.
(c) Reduced porosity increased water repellency which results in decreased infiltration.
Eg:- On a hot summer day near the farms we can see that air above the soil shimmers. It happens because of hot air evaporates the water of the soil and vapour reflects the sunlight. Hence, the air above the soil seems to shimmer.
(iii) Absorption of water by different soil is different.
Experiment 6
Take a plastic funnel. Take a filter paper and place it in the funnel. Pour 50g powdered soil in the funnel. Measures water in a measuring cylinder. Pour water drop by drop in the funnel. Do not pour all water at one place. Keep pouring water till it starts dripping. Note the amount of water left with you. Subtract this amount from the amount you started with. You will get the amount of the water retained by the soil.
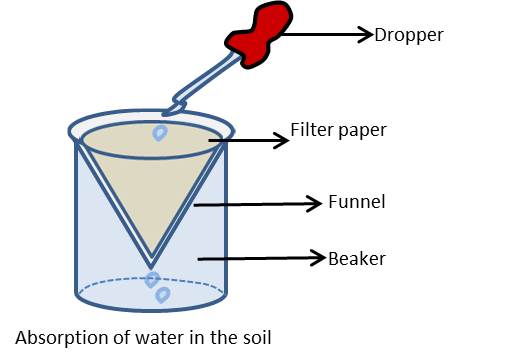
Record results in your note book-
Weight of soil = 50 g
Initial volume of water in the measuring cylinder = U mL
Final volume of water in the measuring cylinder = V mL
Weight of the water absorbed by the soil= (U-V)g
(1mL water has weight equal to 1g)
Percentage of water absorbed = (U-V)x100/50
(i) Sandy soil-
Sandy soil has the highest percolate rate with water. Sandy soil allows water to reach a well faster and in greater amount because it has large particles and less water retention capacity.
(ii) Clayey soil-
Clayey soil has the lowest percolation rate with water. Clayey soil retains the highest amount of water and sandy retains the least water
(iii) We can grow more trees so that we have more rain than evaporation. Hence rain water will percolate more and will reach to water table.
(19) Infiltration –
Infiltration is the entry of water into the surface of the soil.
(20) Climatic factors-
Wind, rainfall, temperature, light and humidity are some important climatic factors which affect the soil profile and determine the various type of vegetation and crops.
(21) Type of soils and crops grown in it is shown table below:
Type of Soil and crops grown –
| S. N. | Type of soil | Crops grown | Remark |
| 1. | Clayey | Cereals(Wheat and gram), paddy, | Soils retain good amount of water |
| 2. | Loamy | Cereals(Wheat and gram),lentils
(masoor) and pulses |
It drain water easily |
| 3. | Sandy- loamy | Cotton | It drains water easily and can hold plenty of air |
(22) Soil erosion-
The process in which fertile soil is removed by wind, water or ice is known as soil erosion. In absence of plants, soil becomes loose. So, soil erosion can easily happen. Soil erosion is more severe in areas of no vegetation or less vegetation such as desert or bare land.
(23) Prevention of soil Erosion-
(i) Prevent cutting of trees
(ii) Prevent deforestation
Helping Topics
Differences Between Clayey Soil and Sandy Soil
Steps to Prevent of Soil Pollution
Benefits of Prevention of Soil Erosion