Notes of chapter: Acids Bases and Salts are presented below. Indepth notes along with worksheets and NCERT Solutions for Class 7.
(1) Acids
Acids are those substances which taste sour. The word acid comes from the Latin word acere which means sour.
Eg:- Lemon, curd, tamarind etc.
A solution is said to be acidic if it has more concentration of hydrogen ion than concentration of hydroxide ion.
H+ >OH–
H+ = hydrogen ion in solution
OH– = hydroxide ion in solution
Eg:- Hydrogen chloride(HCl), Hydrogen sulphuric acid(H2SO4) etc.
The chemical nature of these substances is acidic.
(2) Bases
The substances which are bitter in taste and feel soapy on touching are known as bases. The nature of these substances is said to be basic.
Eg:- Soap, detergent, cleaning agent, baking soda, chalk etc.
A solution is said to be basic if it has less concentration of hydrogen ion than concentration of hydroxide ion.
H+ < OH–
H+ = hydrogen ion in solution
OH– = hydroxide ion in solution
Eg:- Sodium hydroxide (NaOH), Ammonia(NH3), Zinc hydroxide [Zn(OH)2]
Video below is explaining Acids, bases and Salts-
(3) Indicators
Indicators are those substances which can change their colour when added to a solution contains acidic or basic substance. In simple words, indicators are those substances which help us to identify acid and base.
Eg:-Turmeric, litmus, China rose petals etc. are some natural indicators.
(i) Litmus
(a)Litmus is a natural indicator extracted from lichens.
(b)It has mauve colour in the distilled water.
(c) It turns red when added to acidic solution and it turns blue when added to basic solution.
(d)It is available in the form of solution or in the form of strips of paper. It is commonly known as red or blue litmus paper.

Effect of different solutions red and blue litmus paper
(ii) Turmeric
Turmeric is a natural indicator.
Experiment
Take a tablespoonful of turmeric powder. Add a little water and make a paste. Make turmeric paper by depositing turmeric paste on blotting paper/filter paper and drying it. Cut thin strips of the yellow paper obtained. Put a drop of soap solution on the strip of turmeric paper.
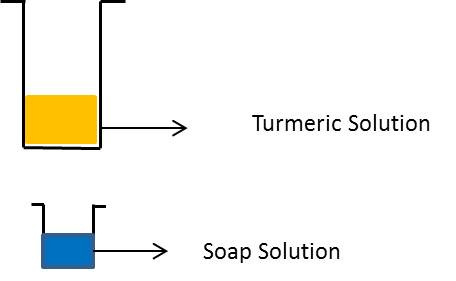
Observation: Soap solution on turmeric paper turns red because turmeric turns red in basic solutions.

Video below is showing how to identify acids and bases by indicators with practicals-
Effect of different solutions on turmeric solution
(iii) China Rose
China rose is a natural indicator.
Experiment
Collect some China rose petals and place them in a beaker. Add some warm water. Keep the mixture for some time till water becomes coloured. Use the coloured water as an indicator. It turns acidic solutions to dark pink and basic solutions to green.

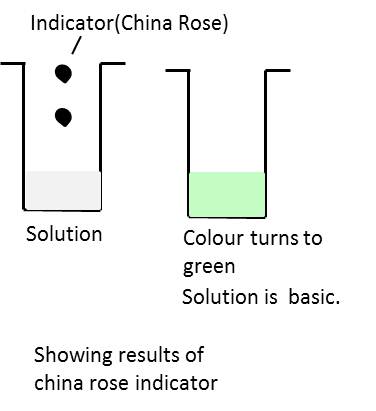
Effect of China rose on different solution
Effect of different indicators on different solutions
(5) Neutral Solutions
Neutral solutions are those solutions which are neither acidic nor basic in nature.
Neutral solutions are those solutions which have equal concentration of hydrogen ion and hydroxide ion.
H+ = OH–
H+ = hydrogen ion in solution
OH– = hydroxide ion in solution
(6) Neutralisation
The process in which an acid and a base neutralise each other and salt and water produce is called neutralisation.
Acid + Base → Salt + Water (heat is evolved)
Hydrochloric acid (HCl) + Sodium hydroxide (NaOH) → Sodium chloride (NaCl) + Water (H2O)
Experiment
Fill ¼ of a test tube with dilute hydrochloric acid. It is a colourless acid. Take phenolphthalein solution in another test tube. It is a colourless solution in acidic and neutral solution. But phenolphthalein solution gives dark pink in basic solution. Now add few drops of indicator phenolphthalein in hydrochloric solution. Solution remains colourless. Now add a drop of sodium hydroxide solution by a dropper .Stir the tube. The colour of solution becomes dark pink as solution is basic in nature now. Add one more drop of the hydrochloric acid in the solution. Shake well test tube. The colour of the tube disappears. When an acidic solution is mixed with a base solution, both the solutions neutralise the effect of each other. Touch the tube immediately after neutrialisation, it is warm. It means that heat is always produced in the reaction.
Neutralisation in everyday life
(i) Indigestion
An antacid such as milk of magnesia neutralise hydrochloric acid of our stomach and we feel relief.
(ii) Ant bite
Ant injects formic acid into our skin which neutralises by rubbing moist baking soda or calamine solution, which contains zinc carbonate.
(iii) Soil treatment
When soil is acidic it is treated by bases like quick lime or slaked lime ( calcium hydroxide) to neutralised acidic effect. When soil is basic it is treated by organic matters which releases acids to neutralised basic effect.
(iv)Factory wastes
The wastes of many factories contain acids. If they are allowed to flow into water bodies, the acid will kill fish and other organisms. The factory wastes are neutralized by adding basic substances.
(7) Salt
A new substance is formed in the neutralisation reaction which is called salt. It can be basic, acidic or neutral in nature.
(8) pH Scale
pH scale is a scale to measure hydrogen ion concentration in a solution.
Limits of pH solution vary from 0 to 14.
where,
0 stand for acidic solution
14 stand for alkaline solution
7 stand for neutral solution
Therefore, values less than 7 are acidic in nature and value greater than 7 are basic in nature.
0 __________________7__________________14
Acidic Neutral Basic
Helping Topics
Differences between acids and bases
Effect of different solutions on red and blue litmus paper
Effect of different solutions on turmeric solution
Effect of china rose on different solution
Effect of different solutions on different indicators